Industrial operators are facing unprecedented financial pressure as regulatory agencies worldwide impose stricter emission standards and escalate penalties for non-compliance. Recent enforcement actions have seen fines reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars, with some operations forced to shut down entirely until they meet environmental requirements. For compliance officers tasked with navigating this challenging landscape, finding reliable solutions that balance regulatory demands with operational efficiency has become critical.
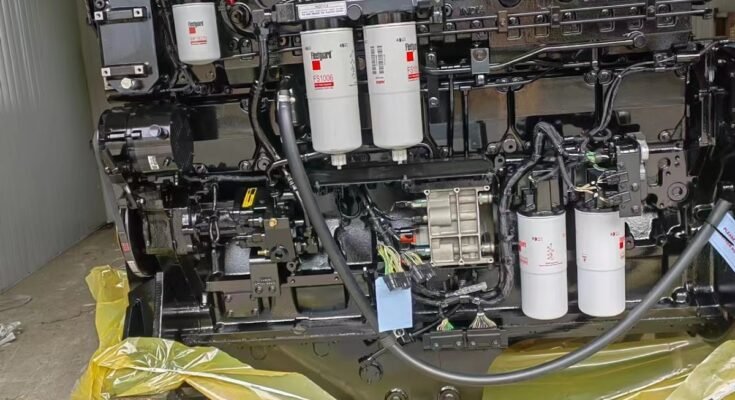
The Cummins QSK23 engine represents a proven answer to this compliance challenge. Engineered specifically for heavy-duty industrial applications, this powerhouse combines exceptional performance with advanced low-emission technology that meets the most stringent global standards. Its sophisticated fuel management systems and integrated emission control features deliver the power industrial operations demand while keeping pollutants well within regulatory limits. This guide provides compliance officers with essential information on leveraging the QSK23 to maintain regulatory compliance, avoid costly penalties, and ensure uninterrupted operations in an increasingly regulated environment.
Understanding Emission Regulations for Industrial Diesel Engines
Industrial diesel engines operate under increasingly stringent emission frameworks that vary by region but share common objectives. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Tier 4 Final standards mandate dramatic reductions in particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, while the European Union’s Stage V regulations impose similarly rigorous limits on non-road mobile machinery. These standards target specific pollutants: nitrogen oxides must not exceed 3.5 grams per kilowatt-hour for engines in the QSK23’s power range, while particulate matter faces even tighter restrictions at 0.02 grams per kilowatt-hour under EPA guidelines.
Compliance officers confront multiple obstacles in meeting these requirements. Legacy equipment often lacks the technological sophistication needed to achieve modern emission thresholds, forcing difficult decisions about retrofitting versus replacement. Testing and certification procedures demand substantial documentation, requiring detailed records of emission performance across varying operational conditions. Many facilities struggle with the technical complexity of selective catalytic reduction systems and diesel particulate filters, which require specialized knowledge for proper operation and maintenance.
The financial consequences of non-compliance extend far beyond initial fines. EPA violations can trigger penalties exceeding $45,000 per day per engine, with cumulative costs quickly reaching seven figures for larger operations. Beyond monetary sanctions, regulatory agencies can issue cease-and-desist orders that halt production entirely until compliance is achieved. Equipment seizures, mandatory recalls, and criminal prosecution for willful violations represent the most severe outcomes. Perhaps equally damaging are the reputational consequences—government contract disqualifications and public disclosure requirements can permanently damage business relationships and market position in an era where environmental responsibility increasingly influences procurement decisions.
Cummins QSK23 Engine: Performance Characteristics and Advantages
The QSK23’s advanced fuel injection architecture forms the foundation of its exceptional efficiency profile. Its high-pressure common rail system delivers fuel at pressures exceeding 2,000 bar, enabling precise control over injection timing and atomization. This sophisticated approach ensures complete combustion, extracting maximum energy from every drop of diesel while simultaneously minimizing unburned hydrocarbons and particulate formation. The system’s electronic control module continuously adjusts injection parameters based on load conditions, altitude, and temperature, optimizing performance across the engine’s entire operating range.
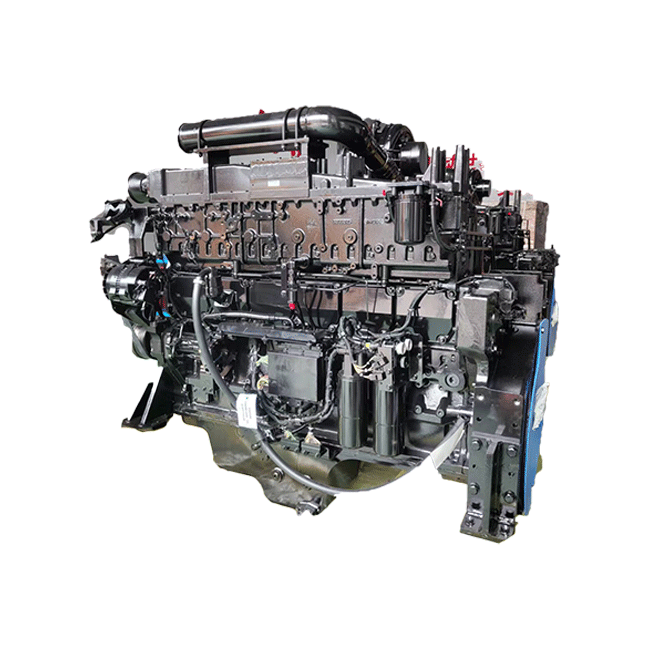
Performance metrics demonstrate why this engine dominates heavy industrial applications. The QSK23 generates up to 800 horsepower with peak torque reaching 3,085 Newton-meters, providing the raw power necessary for demanding operations like large-scale mining, marine propulsion, and stationary power generation. Despite this substantial output, fuel consumption remains remarkably efficient, with brake-specific fuel consumption rates consistently lower than comparable engines in its displacement class. This efficiency translates directly to operational cost savings, with some operators reporting fuel expense reductions of 8-12% compared to their previous powerplants.
Reliability distinguishes the QSK23 from competing industrial engines. Its heavy-duty block construction and reinforced internal components withstand the extreme stresses of continuous high-load operation, with documented service intervals extending beyond 50,000 hours in properly maintained installations. The engine’s modular design simplifies maintenance procedures, reducing downtime during routine servicing. Where emission performance is concerned, the QSK23 achieves regulatory compliance without sacrificing durability—a critical advantage over retrofit solutions that often compromise engine longevity. Independent testing confirms that the QSK23 maintains emission compliance throughout its service life, whereas some competitors experience performance degradation that pushes them toward regulatory thresholds as components age.
How the Cummins QSK23 Meets Low-Emission Requirements
The QSK23’s emission control strategy integrates multiple technologies that work synergistically to reduce pollutants at their source and capture what remains. At the heart of this system lies Selective Catalytic Reduction, which injects diesel exhaust fluid into the exhaust stream where it reacts with nitrogen oxides over a specially formulated catalyst. This chemical process converts harmful NOx into harmless nitrogen and water vapor, achieving reduction rates exceeding 90%. The system’s precise dosing mechanism adjusts fluid injection based on real-time exhaust composition, ensuring optimal conversion efficiency without wasting consumables.
Complementing the SCR system, the QSK23 employs a high-efficiency diesel particulate filter that captures microscopic soot particles before they exit the exhaust. The filter’s advanced ceramic substrate traps particulates while allowing exhaust gases to flow freely, maintaining backpressure within acceptable limits. Automated regeneration cycles periodically burn off accumulated soot, maintaining filter efficiency throughout the engine’s service life without operator intervention. Field data from mining operations demonstrates the effectiveness of this approach—QSK23-powered equipment consistently registers particulate emissions below 0.015 grams per kilowatt-hour, well under regulatory thresholds.
When benchmarked against conventional industrial diesels, the performance gap becomes striking. Older engines without integrated emission controls typically produce nitrogen oxide levels three to five times higher than current standards permit, while their particulate output can exceed limits by factors of ten or more. The QSK23 achieves compliance without the performance penalties associated with retrofit solutions, which often reduce power output by 5-8% and increase fuel consumption. Operators transitioning from legacy equipment report that the QSK23 actually delivers superior performance while simultaneously meeting the strictest emission requirements, eliminating the traditional trade-off between environmental compliance and operational capability.
Steps to Ensure Compliance with the Cummins QSK23
Begin by conducting a comprehensive emissions audit of your existing equipment to establish baseline pollutant levels and identify specific compliance gaps. Engage certified testing professionals to measure nitrogen oxide, particulate matter, and hydrocarbon emissions under actual operating conditions rather than relying on manufacturer specifications for aging equipment. Document current fuel consumption rates, maintenance costs, and any previous regulatory warnings or violations. This audit creates the factual foundation for justifying equipment upgrades to financial stakeholders and provides regulators with evidence of proactive compliance efforts. Map each piece of equipment against applicable standards—EPA Tier levels, EU Stage requirements, or regional regulations—to prioritize replacement decisions based on compliance urgency and operational criticality.
Integration of the QSK23 requires careful planning that extends beyond simple equipment replacement. Coordinate with Cummins-certified technicians to assess installation requirements, including mounting configurations, exhaust routing for aftertreatment systems, and diesel exhaust fluid storage capacity. Verify that electrical systems can support the engine’s electronic control modules and sensor networks, upgrading power supplies if necessary. Schedule integration during planned maintenance windows to minimize production disruptions, and arrange operator training sessions that cover the QSK23’s specific operational characteristics and emission system indicators. Establish supply chains for diesel exhaust fluid and specialized filters before commissioning, ensuring these consumables never interrupt operations due to procurement delays. For facilities requiring comprehensive parts support, authorized distributors like GRT offer extensive inventories of genuine components and technical expertise to support QSK23 installations throughout their operational lifecycle.
Sustained compliance depends on rigorous maintenance protocols that preserve emission system effectiveness throughout the engine’s service life. Implement a documented maintenance schedule that addresses both traditional mechanical components and emission-specific elements like SCR catalysts and particulate filters. Monitor diesel exhaust fluid quality and consumption rates, as contaminated fluid or incorrect dosing immediately compromises NOx reduction. Install remote monitoring systems that track emission-relevant parameters in real-time, alerting maintenance personnel to developing issues before they escalate into compliance violations. Conduct quarterly emission verification tests that confirm continued regulatory adherence, creating an audit trail that demonstrates ongoing compliance commitment to regulatory agencies.
Documentation practices must satisfy both operational needs and regulatory expectations. Maintain comprehensive records of all emission testing results, maintenance activities, and component replacements in formats that regulatory agencies can readily audit. Preserve fuel purchase records, diesel exhaust fluid consumption logs, and operational hour meters that collectively verify proper system operation. Develop standardized reporting templates that compile this information for annual or periodic regulatory submissions, ensuring consistency across reporting periods. Designate a compliance coordinator responsible for maintaining these records and serving as the primary contact for regulatory inquiries, establishing clear accountability within your organization. This systematic approach transforms compliance from a reactive burden into a managed process that protects operations from enforcement actions while demonstrating environmental stewardship to stakeholders and regulators alike.
Achieving Compliance Success with the QSK23
The Cummins QSK23 engine delivers a comprehensive solution for industrial operators navigating the complex landscape of emission regulations. Its integrated low-emission technologies—including advanced SCR systems and high-efficiency particulate filtration—consistently achieve compliance with EPA Tier 4 Final, EU Stage V, and other stringent global standards while maintaining the exceptional power and reliability that demanding industrial applications require. This dual capability eliminates the false choice between regulatory adherence and operational performance that has plagued the industry for years.
Beyond regulatory compliance, the QSK23 generates substantial operational benefits that strengthen the business case for adoption. Reduced fuel consumption translates directly to lower operating costs, while extended service intervals and proven durability minimize maintenance expenses and production disruptions. The avoidance of non-compliance penalties—which can exceed tens of thousands of dollars daily—represents immediate financial protection, but the longer-term advantages of maintaining uninterrupted operations and preserving market reputation prove equally valuable in today’s environmentally conscious business environment.
Proactive compliance represents the only sustainable strategy in an era of escalating regulatory enforcement. Waiting until violations occur exposes operations to financial penalties, operational shutdowns, and reputational damage that far exceed the investment required for compliant equipment. Compliance officers should contact Cummins authorized representatives to conduct site-specific assessments that identify optimal integration strategies for the QSK23, ensuring your operations remain ahead of regulatory requirements while maximizing performance and efficiency in your specific application environment.




