With the rapid expansion of the digital world, the volume of data generating every passing day has taken an unparalleled interest in permanent storage facilities. Whether personal or for business, tech enthusiasts and professionals are increasingly challenged to properly manage these expanding libraries of digital assets, from cherished family photos to business-critical documents. With this in mind, the need for a storage system that delivers massive capacity, steadfast performance and flexible customization options has never been greater.
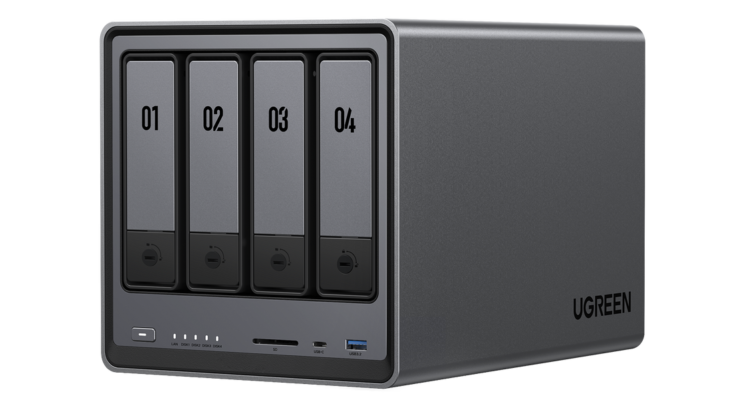
This is where the 4-bay Network Attached Storage (NAS) system comes into play, a robust solution designed to meet these contemporary storage needs head-on. These systems strike a nice balance between consumer-grade external drives and enterprise storage arrays, by delivering the ideal blend of capacity, redundancy, and accessibility. 4-bay NAS units offer enterprise-level power in a consumer-friendly design, thanks to multiple drive bays, high-end RAID configurations and serious management features.
We will discuss the technical specifications that allow these systems to store, search and return, storage space optimization techniques, compelling RAID configurations for any use case, ways to increase storage to the max by selecting and arranging drives strategically. Recognizing these factors is essential in devising a storage solution that not only matches present requirements but also allows for future scalability.
Technical Specifications of NAS 4 Bay Systems
With its x86 architecture, Intel is at the core of every powerful 4-bay NAS system, providing the processing muscle required to fly through file serving, media transcoding and virtualization tasks. Combining this proven architecture, which guarantees extensive software compatibility with proven reliability across a broad spectrum of applications — from home media servers to small business deployments.
Modern 4-bay NAS units, like UGREEN models, feature a quad-core processor and DDR5 RAM, starting at 8GB and expandable up to 64GB for enhanced performance. Such a processing backbone provides seamless multitasking efficiency, with data transfers, media streaming, and surveillance recording all occurring simultaneously without a performance hitch. Even under heavy workloads, you can expect responsive operation as you get efficient processors and sufficient RAM.
High reliability systems are heavily reliant on thermal management. More sophisticated 4-bay NAS designs use airflow channels, variable-speed fans, and temperature monitoring systems that can reduce the speed of the fans for better silence. These CPUs will use the cooling technology in concert to keep optimal operating temperatures while minimizing power consumption. The combination of energy-efficient components and smart power management features lowers power costs without compromising on 24/7 operation capability. With the careful implementation of such thermal/power management systems, even 4-bay NAS systems can be run without excessive power/thermal waste, and also in a virtually silent manner, making these units even more at home both in your home or workspace.
Maximizing Storage Capacity and Customization
Optimizing SATA Drive Bays for Flexibility
Indeed, the real power of any 4-bay NAS lies in their sheer amount of potential storage availability. Given that modern drives can have up to a maximum of 20TB each, a fully populated system can deliver a magical 80TB of raw storage. At this scale, making an informed decision about which drives to select is critical as 16TB drives are great value for money but there may be an argument to select 20TB drives to give you the most capacity headroom for future data growth. The trick is to strike the right balance between immediate storage requirements and long-term scalability options.
For 4-bay NAS setups, SATA drives will always be the best value and most stable for your NAS experience than their NVME counterparts. The SATA interface, though mature, also provides consistent performance for the sequential read/write operations common in NAS workloads. Hot-swappable functionality allows for on-the-fly replacement of the drives without having to power the system down, and the standardized connection makes it possible for drives from different manufacturers to be used interchangeably.
To keep functioning at optimal capacity, your drives need to be managed. SMART checks in real time for health of data on drive, and scheduled disk scrubbing checks bytes for silent data corruption. For the optimal RAID performance while expanding storage, add drives of the same capacity and age. If you need the most flexibility possible, think about using a tiered storage approach, allocating specific drives to specific workloads based on the performance you need. This need for flexibility is achieved through careful planning of storage resources so that the system will be optimal now and in the future as storage requirements change.
RAID Configurations for Performance and Security
Balancing Speed and Redundancy
RAID configurations are the backbone of any NAS 4-bay system that is reliable. RAID 0 is the fastest option, as it stripes data across drives but requires no redundancy. RAID 1 mirrors data across pairs of drives for excellent protection, but at the cost of half your available storage. RAID 5 provides a good balance, ensuring reliability through parity data while retaining most of the storage capacity. For mission-critical data, RAID 10 (a.k.a RAID 1+0 stands for RAID 1 then stripe) is used to provide mirroring and striping for speed and redundancy.
RAID 10 is most beneficial with some small business environments, where rapid database operations and file access is critical. The mirrored striping setup guarantees operations continue in the event two drives fail — as long as they don’t share a mirror set. At the home level, RAID 5 is probably the most common setup, providing maximum storage with protection against single-drive loss. This setup can stream 4K media content, run virtual machines, and host backup services all at the same time.
Modern NAS systems automatically start rebuilding processes when a drive fails. Hot-spare drives can be configured to automatically engage upon drive failure minimizing downtime. Scheduled consistency checks keep RAID 5 arrays free of silent data corruption. Backups still count as essential — RAID gives redundancy, not backups. Having detailed rebuild procedures and testing recovery scenarios means you can implement recovery quickly when things go wrong.
Future-Proofing Your Storage Setup
How to plan expanding your NAS 4-bay system In the simplest case, you replace existing drives made with higher-capacity drives, allowing capacity increases without any additional hardware on top. Look for enterprise-grade replacement drives with higher mean time between failure (MTBF) ratings and greater vibration protection to deliver long-term dependability.
Today, advanced NAS systems are built around the latest file systems, including ZFS, that offer features such as real-time data compression, inline deduplication, and snapshots. Deployments of such technologies maximize end user storage consumption whilst providing a strong level of data protection. ZFS shook the tech world when it introduced powerful self-healing capabilities that automatically detect and repair silent data corruption, enabling data integrity that could withstand years. Because the copy-on-write architecture does not lose data related to sudden power failures, it is ideal for critical storage applications.
Hybrid cloud integration — put your NAS capabilities in the cloud This enables automatic backup of your sensitive data to services such as Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage by implementing cloud sync features. This forms a solid disaster recovery strategy but still ensures quick local access to commonly accessed files. Cloud tiering and similar advanced features port less-accessed data to cloud storage automatically, minimizing local requirements while leaving every file accessible via the NAS interface.
Key Takeaways on NAS 4 Bay Systems
The 4-bay NAS system is a marvel of modern storage technology, representing the sweet spot between performance, capacity, and reliability. This pressurized octa-core from Intel has one of the best RAID configurations and drive bay options, allowing it to be a central part of your home or small business environments. And being able to pair them with ZFS means that these systems can be a part of your future, even if cloud has such a saving grace.
RAID technology allows users to combine multiple disks into a logical storage unit, increasing both capacity and redundancy, ensuring that data remains safe even if one or more drives fail. Data up to October 2023 filter through as training data to fine-tune the system. Whether you dabble in tech and manage a media collection, or are a pro who needs to protect company data, the 4-bay NAS provides enterprise-level features in a convenient, custom platform.